Understanding the Benefits of Plant-Based Eating
Plant-based eating has gained significant attention in recent years, as more and more people are recognizing the numerous health, environmental, and ethical benefits associated with this dietary choice. This article delves into the science behind plant-based diets, the potential health benefits, and how to make the transition to a more sustainable and nutritious way of eating.
What is Plant-Based Eating?
Plant-based eating, also known as a whole-food, plant-based diet, emphasizes foods derived from plants—vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds—with minimal or no animal products. This approach is different from a vegetarian diet, which may still include dairy and eggs, and a vegan diet, which excludes all animal products.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Eating
1. Improved Heart Health
A diet rich in plant-based foods has been shown to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are high in fiber, which can help reduce the absorption of cholesterol.
2. Lower Risk of Certain Cancers
Studies have linked plant-based diets to a lower risk of developing certain cancers, especially those of the digestive system. The antioxidants and phytochemicals in plant foods can help protect against cellular damage that can lead to cancer.
3. Better Digestive Health
The fiber in plant-based foods aids digestion and can help prevent constipation and lower the risk of developing diverticulosis.
4. Weight Management
Plant-based diets tend to be lower in calories and saturated fats, which can contribute to healthy weight maintenance or even weight loss.
5. Diabetes Prevention and Management
A diet high in fiber and low in glycemic index foods can improve blood sugar control and is beneficial for managing or preventing type 2 diabetes.
6. Enhanced Brain Health
Some research suggests that a plant-based diet may improve brain health and even slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
Environmental Benefits
Adopting a plant-based diet can significantly reduce your carbon footprint. Livestock farming is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water use. By choosing plant-based options, you can help combat climate change and promote sustainable food practices.
Ethical Considerations
For many, a plant-based diet is a statement of ethical consideration for animal welfare. By reducing the demand for animal products, you contribute to a more humane and less cruel food industry.
Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
1. Start Slow
Gradually incorporate more plant-based meals into your diet. You might start by having a few meatless meals a week and build from there.
2. Learn to Cook with Plant-Based Ingredients
Experiment with a variety of plant-based ingredients like tofu, tempeh, and a wide array of vegetables, grains, and legumes.
3. Nutrient Considerations
Be aware of nutrients that may be lacking in a plant-based diet, such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, and consider supplementation or fortified foods where necessary.
4. Seek Out Resources
There are numerous resources available, including cookbooks, websites, and support groups, to help you transition smoothly to a plant-based lifestyle.
Conclusion
The journey to a plant-based diet is a personal one, with benefits that extend beyond personal health to the well-being of the planet and its inhabitants. Whether you choose to go fully plant-based or simply incorporate more plant-based meals into your diet, the positive impact can be profound.
For more information and guidance, consider consulting with a registered dietitian or a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable in plant-based nutrition.
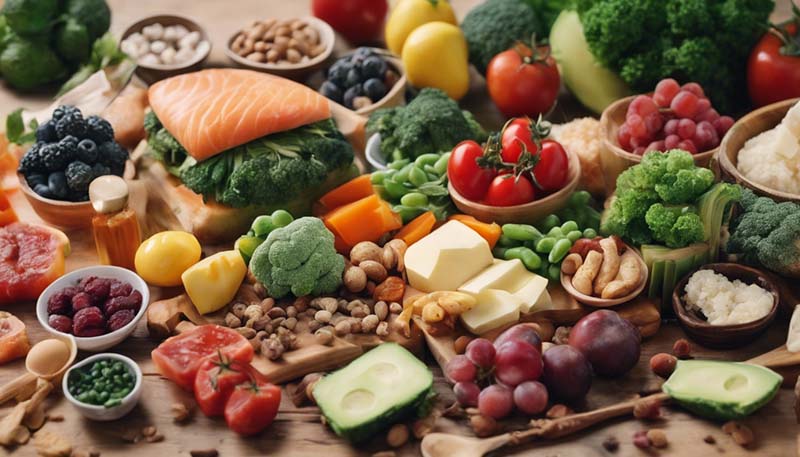





























Leave a comment