Introduction
Chronic inflammation is a common factor in many diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. An anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce the risk of these conditions by promoting overall health and well-being. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on the foods to include and avoid in an anti-inflammatory diet.
Foods to Include
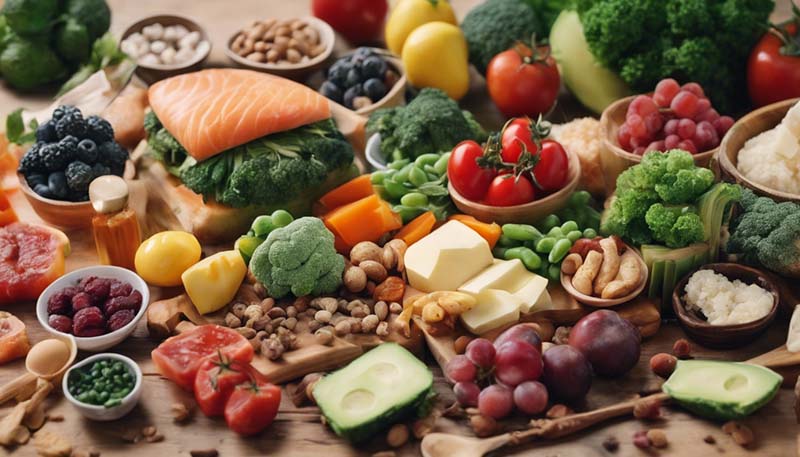
An anti-inflammatory diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins. Here are some key food groups to focus on:
-
Fruits and Vegetables
Choose a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, such as berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and bell peppers. These are packed with antioxidants and vitamins that help reduce inflammation.
-
Whole Grains
Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread. They are rich in fiber, which can help reduce inflammation and improve gut health.
-
Healthy Fats
Include sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon. Omega-3 fatty acids found in these foods are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Lean Proteins
Choose lean protein sources like chicken, turkey, fish, and legumes. These provide essential amino acids that help repair tissues and reduce inflammation.
-
Herbs and Spices
Garlic, ginger, turmeric, and cinnamon are not only flavorful but also have anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporate them into your meals for added health benefits.
-
Tea and Coffee
Drinking green tea and black tea can help reduce inflammation due to their antioxidant content. Coffee, in moderation, can also be part of an anti-inflammatory diet.
Foods to Avoid
While it's important to know what to include in your diet, it's equally important to be aware of foods that can contribute to inflammation. Here are some foods to limit or avoid:
-
Refined Carbohydrates
Limit intake of white bread, pasta, and pastries made with refined flour. These can cause blood sugar spikes and promote inflammation.
-
Sugary Foods and Drinks
Reduce consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages, candies, and desserts. Excess sugar can lead to chronic inflammation and weight gain.
-
Trans Fats
Avoid trans fats found in processed foods, such as margarine, and some baked goods. Trans fats can raise bad cholesterol levels and contribute to inflammation.
-
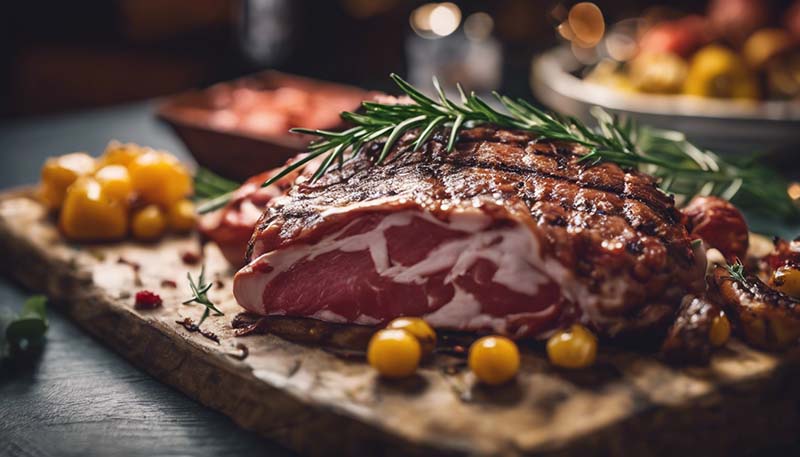
Saturated Fats
Limit saturated fats from fatty meats, butter, and full-fat dairy products. Too much saturated fat can lead to inflammation and increase heart disease risk.
-
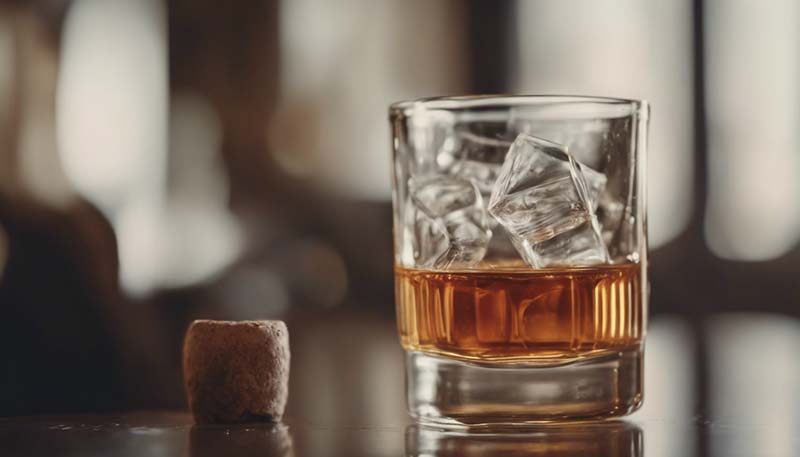
Excessive Alcohol
Alcohol can cause inflammation in the body, especially when consumed in large amounts. It's best to consume alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether.
-
Processed Foods
Minimize processed foods that are high in sodium and additives, which can contribute to inflammation and have negative effects on overall health.
Conclusion
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet is a proactive approach to improving your health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and avoiding pro-inflammatory foods, you can support your body's natural ability to fight inflammation and maintain a healthy lifestyle.





























Leave a comment