Introduction
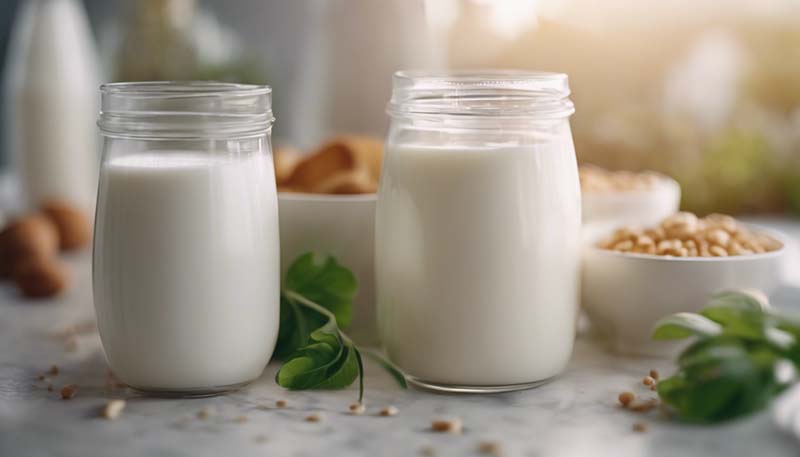
The global market for plant-based milk has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by consumer demand for healthier, more sustainable, and ethical food choices. This article explores the factors behind the rise of the plant-based milk market, the various types available, their health benefits, the challenges faced by the industry, and the future outlook for this burgeoning sector.
Factors Driving Growth
The rise of the plant-based milk market can be attributed to several key factors:
- Health and Nutritional Concerns: Many consumers are seeking alternatives to dairy milk due to concerns about lactose intolerance and the fat content in cow's milk.
- Environmental Impact: The production of dairy milk has a significant environmental footprint, and plant-based milks are considered more sustainable options.
- Ethical Considerations: Animal welfare is a growing concern, and some consumers prefer plant-based milks for ethical reasons.
- Food Allergies and Intolerances: Plant-based milks cater to those with allergies or intolerances to dairy products.
- Taste and Variety: The development of new and innovative plant-based milk flavors and formulations has broadened their appeal.
Types of Plant-Based Milk
There is a wide range of plant-based milk options available, each with its unique nutritional profile and taste:
- Almond Milk: Low in calories, high in vitamin E, and popular for its subtle, nutty flavor.
- Soy Milk: High in protein and a common choice for those avoiding dairy due to lactose intolerance.
- Oat Milk: Environmentally friendly, with a creamy texture and naturally sweet taste.
- Coconut Milk: Rich in medium-chain fatty acids and a popular choice for its tropical flavor.
- Pea Milk: A newer entry, pea milk is high in protein and has a mild taste.
- Hemp Milk: Packed with omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, hemp milk is a nutritious option.
- Rice Milk: Hypoallergenic and often used in recipes for those with multiple food allergies.
Health Benefits
Plant-based milks offer several health benefits, including:
- Lactose Intolerance Relief: Ideal for those who cannot digest lactose.
- Lower in Saturated Fat: Generally have less saturated fat compared to dairy milk.
- Cholesterol-Free: Most plant-based milks are naturally free of cholesterol.
- Vegan and Vegetarian Diets: Suitable for those following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle.
- Versatility in Cooking and Baking: Can be used as a direct substitute in many recipes.
Challenges and Solutions
The plant-based milk market faces several challenges:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Some plant-based milks lack certain nutrients found in dairy milk, such as calcium and vitamin D. Solution: Fortification of plant-based milks with essential nutrients.
- Environmental Concerns: While more sustainable than dairy, some plant-based milks, like almond milk, require significant water resources. Solution: Encouraging water-efficient farming practices and supporting alternative crops.
- Taste and Texture Variations: Some consumers find the taste and texture of plant-based milks unfamiliar. Solution: Continued innovation in flavor and texture to match consumer preferences.
Future Outlook
The future of the plant-based milk market looks promising, with:
- Increasing Consumer Awareness: As more people become aware of the health and environmental benefits, demand is expected to rise.
- Innovation in Products: New plant-based milk varieties and improved formulations are likely to cater to a wider range of tastes and dietary needs.
- Technological Advances: Technological improvements in processing and packaging will enhance the shelf life and accessibility of plant-based milks.
- Global Expansion: As the market matures in the West, there is significant potential for growth in emerging markets.



























Leave a comment